In the vast landscape of web hosting, choosing the right solution is akin to laying the foundation for your digital presence. Two prominent players in this realm are Virtual Private Servers (VPS) and Cloud Hosting. While both serve the purpose of facilitating online activities, they each bring a unique set of attributes to the table. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricate differences between VPS and Cloud Hosting, helping you make an informed decision for your hosting needs.
Definition of VPS (Virtual Private Server)
In the intricate realm of web hosting, a Virtual Private Server (VPS) stands as a versatile and powerful solution. At its core, a VPS is a virtualized instance within a physical server. It operates as an independent server, providing users with dedicated resources while existing within the framework of a larger physical server.
According to marketsandmarkets.com, The global virtual private server market size is expected to grow from USD 2.4 billion to USD 5.0 billion by 2023.

VPS Hosting: Key Features and Characteristics
1. Isolation
A defining feature of VPS is its ability to offer a private and isolated environment for users. Unlike shared hosting, where multiple websites share resources, a VPS provides a partitioned space exclusively for the user.
2. Root Access
Users enjoy root access, granting them full control over the server’s operating system and configurations. This level of control empowers users to install custom software and make personalized adjustments.
3. Dedicated Resources
VPS hosting allocates dedicated resources such as computing power, RAM, and storage to each virtual instance. This ensures consistent performance even during traffic spikes.
4. Customization
VPS environments are highly customizable. Users can tailor server settings and configurations to meet the specific requirements of their applications or websites.
5. Scalability
VPS solutions often offer scalability, allowing users to scale their resources up or down based on changing needs. This flexibility is particularly valuable for businesses with varying levels of demand.
Advantages of VPS Hosting
1. Enhanced Performance
Compared to shared hosting, VPS hosting offers superior performance. With dedicated resources, users experience faster loading times and improved overall responsiveness.
2. Control and Customization
Root access provides users with a high degree of control, allowing them to configure the server environment according to their preferences. This level of customization is especially beneficial for advanced users and businesses with specific requirements.
3. Isolation and Security
The isolation provided by VPS ensures that the actions of other users on the same physical server have minimal impact. This enhances security by reducing the risk of vulnerabilities associated with shared hosting environments.
4. Cost-Efficiency
While more expensive than shared hosting, VPS hosting offers a cost-effective middle ground between shared and dedicated hosting. Users benefit from dedicated resources without the significant costs associated with a dedicated server.
Limitations of VPS Hosting
1. Technical Expertise
Utilizing a VPS may require a certain level of technical expertise, especially for tasks such as server management, software installations, and troubleshooting.
2. Resource Limits
While dedicated, resources on a VPS are finite. In scenarios of exceptionally high traffic or resource-intensive applications, users may still encounter limitations compared to a dedicated server.
3. Cost Comparisons
Although cost-effective, VPS hosting may not be the most economical option for small websites or applications with minimal resource requirements when compared to shared hosting.
Read More : Factors to consider when choosing a Cloud Hosting Plan
Definition of Cloud Hosting
In the contemporary landscape of web hosting, Cloud Hosting emerges as a transformative force. Unlike traditional hosting solutions, Cloud Hosting harnesses the power of a distributed network of virtual and physical servers to deliver resources dynamically. This innovative approach allows for unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and reliability.
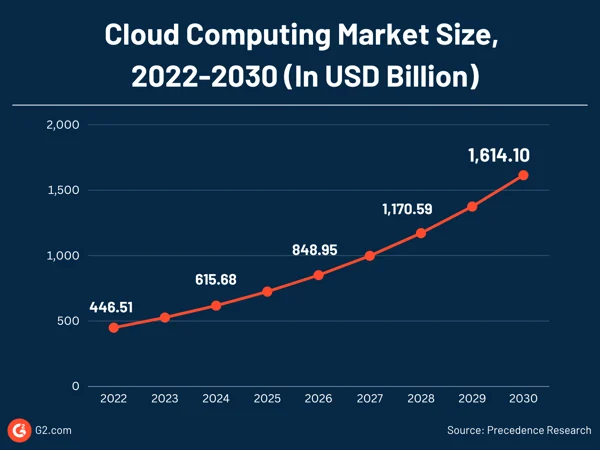
According to G2.com, The global cloud computing market is expected to reach $1.614 trillion by 2030, up from $446.51 billion in 2022.
Cloud Hosting : Key Features and Characteristics
1. Scalability
A hallmark feature of Cloud Hosting is its ability to scale resources seamlessly. Users can increase or decrease computing power, storage, and bandwidth in real-time, ensuring optimal performance during varying workloads.
2. Resource Distribution
Cloud Hosting distributes resources across multiple servers. This not only enhances reliability but also ensures that a failure in one server does not result in service disruption.
3. Flexibility
Cloud environments are inherently flexible. Users can adapt resources to match their requirements, making it an ideal solution for businesses with dynamic computing needs.
4. High Availability
Cloud Hosting is designed for high availability. With resources distributed across a network, there’s a reduced risk of downtime, ensuring that applications and websites remain accessible.
5. Cost Efficiency
Cloud Hosting often operates on a pay-as-you-go model. Users only pay for the resources they consume, making it a cost-effective choice, especially for startups and businesses with fluctuating resource needs.
Advantages of Cloud Hosting
1. Scalability and Performance
The ability to scale resources on-demand ensures that businesses can meet increased traffic or workload requirements without disruptions, resulting in consistent performance.
2. Cost-Effective
The pay-as-you-go pricing model allows users to control costs by paying only for the resources they use. This cost efficiency is particularly advantageous for startups and businesses with variable workloads.
3. Redundancy and Reliability
Cloud Hosting implements redundancy by distributing data across multiple servers. This not only enhances reliability but also mitigates the impact of hardware failures.
4. Global Accessibility
Cloud Hosting enables users to access resources and data from anywhere with an internet connection. This global accessibility is invaluable for businesses with a distributed workforce or an international user base.
Limitations of Cloud Hosting
1. Dependency on Internet Connectivity
Cloud Hosting relies on internet connectivity. If the internet connection is unstable or experiences downtime, it may impact access to cloud resources.
2. Potential Security Concerns
The distributed nature of Cloud Hosting introduces security considerations. While cloud providers implement robust security measures, users must also take precautions to secure their data.
3. Learning Curve
Transitioning to Cloud Hosting may involve a learning curve, especially for users accustomed to traditional hosting solutions. Understanding cloud architecture and management tools is crucial for maximizing benefits.
Comparison: VPS vs. Cloud Hosting
| Feature | VPS Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
| Infrastructure | Virtualized instance within a single physical server. | Utilizes a network of interconnected virtual and physical servers. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability. Users may need to upgrade their VPS for increased resources. | Highly scalable. Resources can be scaled up or down on-demand. |
| Resource Allocation | Dedicated resources allocated to each VPS. | Resources are dynamically distributed across multiple servers. |
| Isolation | Offers a level of isolation, but shares the same physical server with other VPS instances. | Provides isolation through virtualization and distributed architecture. |
| Customization | Users have significant customization capabilities, including installing custom software. | Customization options may be more limited compared to VPS. |
| Control | Users have root access, allowing full control over server configurations. | Users have control over their allocated resources but may not have root access. |
| Performance | Superior performance compared to shared hosting, but may vary based on allocated resources. | Excellent performance, especially during traffic spikes, due to dynamic resource allocation. |
| Cost Structure | Generally more affordable than dedicated hosting but may have a fixed cost. | Typically operates on a pay-as-you-go model, where users pay for the resources they consume. |
| Dependency on Hardware | Dependent on the physical server’s hardware capabilities. | Less dependent on individual server hardware; resources can be distributed across various servers. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for businesses that need more control and predictability in resource allocation. | Suited for businesses with fluctuating workloads and dynamic resource needs. |
| Global Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. | Offers global accessibility, beneficial for businesses with a distributed workforce or international users. |
Use Cases: Choosing Between VPS Hosting and Cloud Hosting
Whether you’re considering VPS (Virtual Private Server) hosting or Cloud Hosting, understanding their ideal use cases is crucial. In this section, we explore the scenarios where each shines, helping you make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
Ideal Scenarios for VPS Hosting
1. Stable Workloads with Predictable Resource Needs
VPS hosting is well-suited for businesses with stable workloads and predictable resource requirements. If your website or application experiences consistent traffic patterns and you need a dedicated environment, VPS provides the necessary control without the complexity of a dedicated server.
2. Budget Constraints with a Need for Control
For businesses on a budget that still require a higher level of control over their hosting environment, VPS strikes a balance. It offers dedicated resources at a more affordable cost compared to dedicated hosting, making it an attractive option for cost-conscious ventures.
3. Applications Requiring Custom Software Installations
If your operations rely on specific software configurations that might not be supported in a shared hosting environment, VPS is a compelling choice. With root access and customization options, VPS allows you to install and configure custom applications tailored to your business requirements.
4. Security-Conscious Applications
VPS hosting provides a higher level of security compared to shared hosting. If your application handles sensitive data or requires a secure environment, the isolation offered by VPS can enhance data protection.
Situations Where Cloud Hosting Excels
1. Fluctuating Workloads and Dynamic Resource Needs
Cloud Hosting shines in scenarios where workloads are variable and unpredictable. The ability to scale resources up or down in real-time ensures that you only pay for what you use, making it an ideal choice for businesses with fluctuating demand.
2. High-Traffic Websites and Applications
Websites or applications that experience sudden spikes in traffic, such as during promotions or events, benefit from the scalability of Cloud Hosting. Resources can be quickly scaled to accommodate increased demand, ensuring optimal performance.
3. Global Businesses with Distributed Teams
Cloud Hosting’s accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection is advantageous for businesses with a distributed workforce. It enables seamless collaboration and access to resources across geographical locations.
4. Cost-Efficiency for Startups and Small Businesses
Startups and small businesses with limited budgets may find the pay-as-you-go model of Cloud Hosting more cost-effective. The ability to scale resources based on current needs allows for cost control and efficient resource utilization.
5. Data Redundancy and High Availability
Cloud Hosting, with its distributed architecture, ensures high availability and data redundancy. In scenarios where data integrity and continuous availability are critical, Cloud Hosting provides a robust solution.
Frequently Asked Questions on VPS vs. Cloud hosting
1. Is VPS a Cloud Server?
While VPS (Virtual Private Server) shares similarities with cloud servers, they are not identical. VPS is a virtualized server within a single physical server, providing dedicated resources. Cloud servers, on the other hand, leverage a network of interconnected servers (virtual and physical) to distribute resources dynamically. The key difference lies in the infrastructure and scalability.
2. Is cloud hosting cheaper than VPS?
The cost comparison between cloud hosting and VPS depends on specific requirements. Cloud hosting often operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing users to pay for resources consumed. VPS may have a fixed cost but can be more budget-friendly for stable workloads. For variable workloads and scalability, cloud hosting’s pay-as-you-go model can be more cost-efficient.
3. What is the difference between VPS and cloud dedicated server?
VPS and cloud dedicated servers share the concept of virtualization but differ in infrastructure. VPS is a virtualized instance within a single physical server, offering dedicated resources. A cloud dedicated server refers to a single virtual server within a cloud infrastructure, allowing for dynamic resource allocation across multiple servers. Cloud dedicated servers provide enhanced scalability and redundancy compared to traditional VPS.
4. Why should I choose VPS hosting?
VPS hosting is an excellent choice for those who need more control and customization than shared hosting. Reasons to choose VPS include:
- Dedicated Resources: Enjoy dedicated computing power, RAM, and storage.
- Control: Users have root access, enabling full control over server configurations.
- Customization: Install custom software and configure the server to meet specific needs.
- Enhanced Performance: Superior performance compared to shared hosting.
5. Which web hosting is right for you?
Choosing the right web hosting depends on factors such as:
- Workload Stability: For stable workloads, VPS might be suitable.
- Scalability Needs: Cloud hosting is ideal for fluctuating workloads.
- Control and Customization: If you need full control, VPS is a good choice.
- Budget Constraints: Consider the cost implications of both VPS and cloud hosting.
- Technical Expertise: Your comfort level with server management may influence your choice.
Conclusion
As we navigate the digital sky, the choice between VPS and Cloud Hosting is influenced by your specific needs, budget constraints, and growth expectations. VPS offers controlled environments and customization, suitable for stable workloads, while Cloud Hosting’s dynamic scalability caters to businesses with variable demands. Ultimately, the decision rests on aligning the hosting solution with your unique journey through the digital cosmos.
Elevate your hosting experience with Rivell
At Rivell, we redefine hosting solutions, offering a seamless blend of performance, reliability, and innovation. Whether you opt for the tailored control of VPS or the dynamic scalability of cloud hosting, Rivell ensures your digital journey is backed by cutting-edge technology and unwavering support.
Explore the possibilities with Rivell and embark on a hosting experience that transcends boundaries. Contact us today.